
The PPC vs. SEO debate is one of the most common concerns people have before hiring a PPC agency. The method you select is a critical decision that determines whether you get the results you need from your marketing investment, impacts how much you spend, and influences how quickly you get results.
On this page, we’ll give you a full breakdown of PPC vs. SEO, including how they work, the pros and cons of each, and how to determine which one aligns with your business and marketing goals.
How PPC Works
PPC is short for pay-per-click. It’s a form of digital advertising that sends paid traffic to a web property, such as a business website. You pay each time someone clicks on your ad.
Types of PPC Advertising
There are many types of PPC advertising. A few of the most common are outlined below.
Search Ads
Most articles about PPC only focus on search ads. These are the ads that appear on search engines like Google and Bing alongside organic (unpaid) search results.
Display Ads
Ads that include text and images or videos are called display ads. These can appear virtually anywhere on the net. The Google Display Network is the largest platform and reaches 90 percent of internet users worldwide, Google reports.
Video Ads
Most of the major ad networks also allow you to run video ads. These can appear across the net as well and often perform better than display ads.
Steps Involved in PPC Advertising
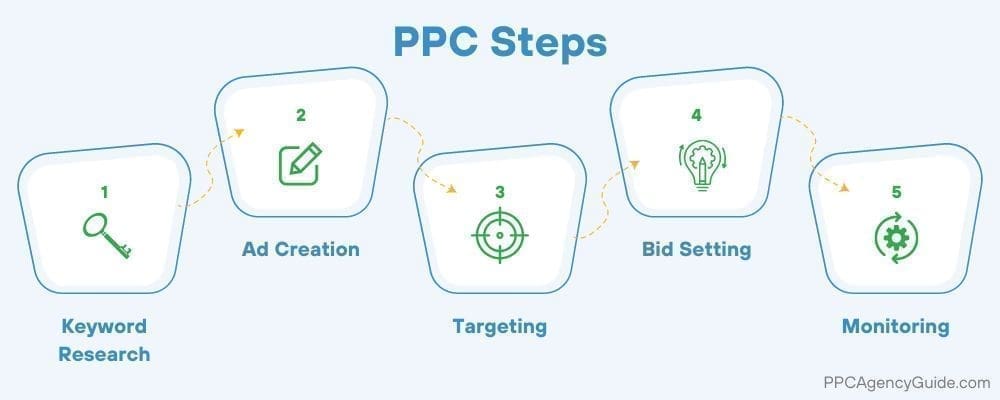
PPC advertising draws from multiple skill sets and is usually handled by a team. Because of this, most businesses work with a PPC agency rather than managing it in-house. A high-level overview of the tasks involved is provided below.
1. Keyword Research
Keyword research is specific to search ads. It involves identifying which search queries should trigger your ad to display.
2. Ad Creation
Most ads are written by a copywriter with the help of a graphic designer or video producer. To enhance the performance of ads, most link to a specialized landing page as well. This aspect typically requires the assistance of a developer.
3. Audience Targeting
You can target who sees your ads with a high degree of precision if you have good data. At a basic level, you can narrow by location, age, and other demographics.
4. Bid Setting
The bid-setting process involves evaluating how much you’re willing to pay for your ad to appear. Your bid can be set to scale automatically based on your chosen factors. Ad networks consider things such as your bid, ad quality, and match before displaying your ad.
5. Monitoring and Adjusting
You or your PPC agency must monitor the performance of the ads and make minor adjustments. This continuous optimization ensures ad performance, and ROI improves over time.
Pros and Cons of PPC
Now that we’ve covered how PPC works, let’s explore some of the pros and cons of PPC.
Pros of PPC
- The ROI of PPC is strong. On average, PPC returns $2 for every $1 spent, according to TechJury.
- PPC provides instant results. You can start generating leads and sales as soon as your ads begin running.
- Your campaigns can be set to focus on people with the intent to buy. This helps ensure your efforts are fruitful.
- You can amass a lot of data quickly. Whether you want to know which offer resonates with people best or quickly define your core audience or what matters most to them, you can find out what you need in a matter of days or weeks.
Cons of PPC
- PPC tends to have a greater investment at the onset. With PPC, the work mainly shifts to the start of the campaign when you’re getting set up, so you’ll incur greater expenses at the beginning.
- You must keep paying to keep seeing results. Even though PPC has benefits like brand awareness that tend to stick, the leads and sales generated by your PPC ads will cease entirely as soon as you stop paying for them.
- It’s hard to learn PPC. It’s easy to make mistakes that eat away at your budget unless you have specialized training.
- PPC requires regular updates. PPC ads need ongoing work, from minor optimization tweaks to full ad refreshes.
How SEO Works
When someone types a query into Google or another search engine, the application uses an algorithm to serve up the best possible results. Search engines don’t tell us everything they’re looking for to prevent websites from gaming the system and artificially landing at the top of search results. However, we know that they look at the user’s history and query to gauge what the person wants to know and evaluate websites to determine which is the best fit. Some signals search engines look for when deciding which results to serve and in what order include the quality of the content, authoritativeness or trustworthiness of the source, and the overall experience the site provides.
Overall, 28 percent of people click on the first result in Google, according to Search Engine Land. Roughly 16 percent click on the second result, and 11 percent click on the third. Listings closer to the bottom of the page receive less than three percent of clicks and almost nothing after the first page is clicked. That means to maximize your organic search traffic, you want to ensure your site appears in search results, and is as close to the top of the list as possible. SEO, short for search engine optimization, is a process or series of tasks dedicated to making that happen.
Steps Involved in SEO

SEO also draws from various skill sets, so it’s often performed by a team or SEO agency. A few aspects involved in a typical SEO strategy are outlined below.
1. Keyword Research
The keyword research performed for SEO is similar to the research conducted for search ads. You must determine which terms people search for that relate to your business. With search ads, however, you can get your ad to appear for specific terms regardless of what your competition is doing if you’re willing to pay more and provide a good experience. With SEO, this is rarely the case. You have to be the authority on a topic to be listed first. If you’re competing against other well-established sites and have been publishing high-quality content about that topic for some time, you may not be able to outrank them for years, if at all. Because of this, keyword research often involves finding a balance: knowing which terms you can reasonably capture and building a strategy around those, as well as working toward capturing some of the more difficult ones over time.
2. On-Page SEO
Sometimes referred to as on-site SEO, on-page SEO relates to optimizing the site, often in ways that visitors will notice. This bracket includes things like site content, tags, and links to other pages of your site.
3. Off-Page SEO
Also referred to as off-site SEO, off-page SEO relates to demonstrating that your site is trustworthy or the authority on a topic. Search engines look for links to your site from other sites as evidence of this, so off-page SEO activities include things like link-building strategies, social media, reviews, and creating sharable content.
4. Technical SEO
Technical SEO can be broken up into two broad categories: things that make it easier for search engines to crawl and understand your site, and things that provide a better user experience. For instance, a site map makes it easy for a search engine to find all your pages. It uses that instead of hopping from one link to the next, which helps ensure no pages are missed. The use of structured data makes it easy for search engines to understand what something means. It’s how Google can display showtimes or recipes, among other things, directly in search results.
Aspects of technical SEO that relate to improving the user experience include things like ensuring pages load fast and work well on mobile devices.
Pros and Cons of SEO
You should have a basic understanding of how SEO works. Now, let’s look at some of the pros and cons of SEO.
Pros of SEO
- It delivers strong ROI. Many organizations have tried to quantify the ROI of SEO with varying levels of success. An e-commerce company will generate around $2.75 for each $1 spent, according to Moz. Other studies have shown similar results and note that e-commerce tends to have the lowest ROI. Other industries range from $6 to $15, per First Page Sage.
- SEO produces long-term results. The work you do towards SEO doesn’t evaporate even if you stop optimizing, so it tends to deliver more stable traffic over time.
- You can reach people at every stage of the buyer’s journey cost-effectively. People tend to start their searches looking for basic information or possible solutions to a problem. You can address these things in your content to catch people at the early stages before they’re ready to buy.
- SEO helps build brand awareness and trust. With SEO, you can introduce your brand to new audiences and educate them to build rapport.
Cons of SEO
- It can take months to see results. There are lots of working parts. The search engine needs to crawl and index your pages first. Then, it takes time and more effort to build up credibility as an authority and overtake sites already ranking for your terms.
- Most industries don’t see ROI until around a year. SEO activities snowball. The more you work at it and the more you do, the bigger your results will be. This also means that brands invest in SEO for about a year before they break even, according to First Page Sage.
- Algorithm shifts can kill your traffic overnight. Google makes thousands of changes to its algorithm every year, according to Search Engine Journal. Some of the bigger ones completely change rankings overnight, creating significant problems for businesses dependent on the traffic.
- You must keep working at SEO. Even though your efforts are still in place, if you stop optimizing, other sites will continue to try to overtake you in search results, and the algorithms will shift. You need to keep working at SEO to maintain rank.
Key Differences Between PPC vs. SEO
PPC and SEO have many similarities. They can both bring you traffic to grow your business and deliver solid ROI, especially if you have an SEO or PPC agency helping. But, there are some key differences between PPC vs. SEO that will impact your decision about which to use.
Timeframe
PPC ads work immediately, while SEO takes time to send you traffic.
Cost
SEO is usually cheaper in the long run, but this largely depends on your niche and what your competitors are willing to spend for their ads to display since the bulk of your costs is based on a bidding system.
Reach
Most people believe SEO provides greater reach because your site can appear in a variety of searches that relate to your brand or content you’ve created. Plus, you can reach people throughout the buyer’s journey. That is often true, especially considering you can choose who sees your PPC ads. However, options like video and display ads let you reach people who aren’t necessarily looking for your products or services, too.
Conversions
PPC is typically conversion oriented. You’re trying to get someone to purchase, fill out a form, or take a specific action. Campaigns are designed to accomplish that task, so they target people who are ready to buy. SEO can lead to more sales, but it’s better for generating awareness and building trust.
ROI
While both PPC and SEO will deliver a return on your investment when managed effectively, the ROI of SEO is generally higher.
How PPC and SEO Work Together
In most cases, it’s not a question of PPC vs SEO. They’re used together to amplify the results.
You Can Dominate Search Results for Branded Terms
You should rank first in search engines for any branded terms, such as the name of your company and products. However, competitors and resellers can sometimes use the same terms to get their search ads to display before your organic listing. When you run PPC ads for branded terms, you have more assurance that people will visit your site when they want to find you instead of a reseller or competitor.
You Can Reach More People at Different Stages
While you can use PPC ads to reach people in the early stages of the buyer’s journey, and content-based ads like boosted posts on Facebook do just this, your readers aren’t likely to purchase right away. By investing in SEO as well, you can use your site to carry people through the buyer’s journey and paid ads to seal the deal.
You Can Boost Conversions
You can use remarketing and retargeting to encourage previous visitors or customers to come back and pick up where they left off. This boosts conversions exponentially.
You Can Make More Informed Decisions
As you run PPC campaigns, you may find that some keywords get a lot of clicks but never convert. It’s a sign that these are helpful terms that people want more information on and are worth covering but keeping them as PPC keywords is not cost-effective. You can meet the needs of your audience by shifting these terms to your SEO strategy instead.
You can also use your PPC data to make better decisions about your SEO. For instance, through A/B testing on your PPC campaigns, you may discover that people prefer a specific offer or are more likely to click a particular color button. Apply these changes to your site to boost conversions for your organic traffic too. Equally, you might learn that the audience you’re attracting through organic search doesn’t align with your PPC targeting. You can try targeting the new audience with your PPC ads to see how they respond and potentially increase conversions too.
PPC vs. SEO: Which is Better
In the battle between PPC vs. SEO, neither is better. They just work differently and are better together. While it’s ok to start with SEO because it takes longer to see results, most businesses can’t afford to wait. PPC, therefore, should also be an early strategy. That way, you begin growing your company quickly and can funnel your ROI into more ads or other long-term strategies.
Work with an Experienced PPC Agency
An expert will ensure your ads are set up right, so they start working faster and generate top ROI. If you’d like to learn more or get started, request a consultation.


















